Java Swing分割、合并文件软件
SwingRandomAccessFileadmin 发布于:2017-02-14 22:15:27
阅读:loading
这里说道的分割、合并文件是将一个文件按照一定的字节大小进行拆分,拆成特定大小的碎片文件,并且将这些碎片文件再还原为原始文件的过程。
今天找了一点点时间将之前写好的程序进行了一个粗略的整理,并将它包装成一个exe文件,看上去像一个软件工具了。主要涉及到的技术点为:swing、序列化、RandomAccessFile随机读写文件、Java打包成exe等。
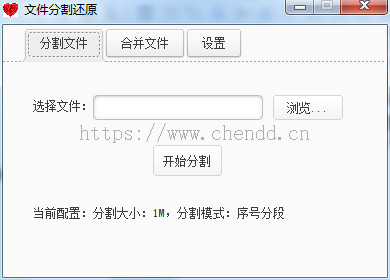
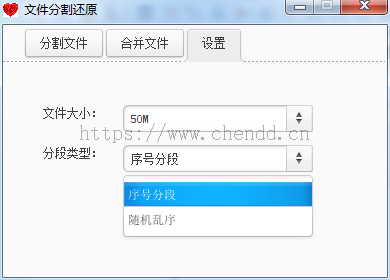
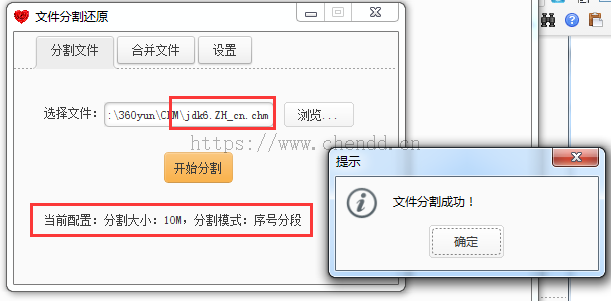
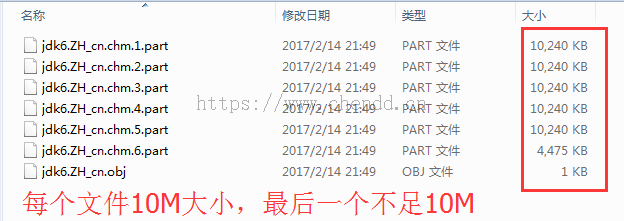
文件分割表示按某些特定的大小将一个文件进行拆分,拆成多个碎片文件,每个碎片表示为一个片段,本例中实现的文件大小参数有:1M、10M、50M、100M,碎片分类为序号分段、随机乱序。举个例子说,如果将一个10M的文件按照1M的大小进行分割,如果使用序号分段则会生成xx1~xx2...等xx10个片段文件;否则如果使用随机乱序则会xx1001,xx5312,xx3322...等一些无规则的随机数字,让人无从得知将怎么恢复文件,稍微能够起到一丢丢的安全提升。
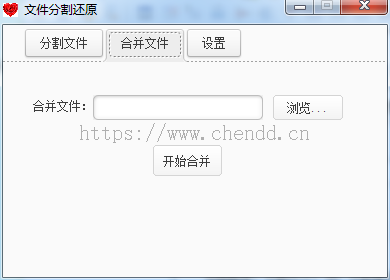
合并文件根据分割文件时生成的配置文件而来,配置文件中记录了所有碎片文件生成时的顺序,依次读取这些碎片文件,并将这些碎片文件写入一个新的文件即可。


打包成exe的时候从MyEclipse安装目录中随便找了一个ico文件,文件打开后状态栏的图片和logo使用了一个玫瑰图片,这都不是重点。
package cn.chendd.core;
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.swing.JOptionPane;
/**
* 按指定文件大小分割文件,并记录文件分割信息
* @author chendd
*
*/
public class SplitFile {
private long blockLength;//分割单个文件大小,参与运算
private long currentTotal;//当前分割次数的位置
private Map<String , Object> propMap;//记录本次分割文件的信息
private boolean order;//排序,true为顺序写入,false为随机写入
public SplitFile(long blockLength , boolean order) {
this.blockLength = blockLength;
propMap = new HashMap<String , Object>();
this.order = order;
}
public boolean split(File srcFile , String splitFolder) throws Exception {
RandomAccessFile raf = null;
try {
long fileLens = srcFile.length();//文件大小
if(fileLens <= this.blockLength){
//System.out.println("分割的文件大小 " + this.blockLength + " 大于文件的大小!");
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "设置要分割的文件大小 " + (this.blockLength / 1024 / 1024) + "M 大于文件的大小!",
"警告", JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE);
return false;
}
raf = new RandomAccessFile(srcFile, "r");
//根据分割块大小,计算一共有多少块文件
int blockCount = (int) (fileLens % this.blockLength);
if(blockCount == 0){
blockCount = (int) (fileLens / this.blockLength);
}else{
blockCount = (int) (fileLens / this.blockLength) + 1;
}
//按快进行读取文件
String srcFileName = srcFile.getName();
//记录源文件名称
propMap.put("fileName" , srcFileName);//原始文件名称
propMap.put("fileLength" , this.getFileLength(srcFile));
propMap.put("fileSuffix" , this.getFileSuffix(srcFileName));
List<String> partList = new ArrayList<String>();
for(int i=0 ; i < blockCount ; i++){
String label = null;
if(order){
label = (i + 1) + "";
} else {
//不考虑会出现重复的
label = (10000 + (int)(Math.random() * 10000)) + "";
}
File destFile = new File(splitFolder + File.separator + srcFileName + "." + label + ".part");
String partFileName = destFile.getName();
partList.add(partFileName);
splitFileDetail(destFile , raf);//分割文件
}
propMap.put("partList" , partList);//碎片文件列表
//记录还原文件相关的数据,用序列化文件
writePropFile(propMap , srcFile , splitFolder);
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new Exception(e);
} finally{
if(raf != null){
try {
raf.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
/**
* 将记录的文件相关的数据写入文件
* @param propMap 写入文件属性对象
* @param srcFileName 源文件名称
*/
private void writePropFile(Map<String, Object> propMap , File srcFile , String splitFolder)
throws Exception{
String newName = srcFile.getName();
int nameIndex = newName.lastIndexOf(".");
if(nameIndex != -1){
newName = newName.substring(0, nameIndex);
}
File propFile = new File(splitFolder, newName + ".obj");
ObjectOutputStream ois = null;
try {
ois = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(propFile));
ois.writeObject(propMap);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new Exception(e);
} finally{
if(ois != null){
try {
ois.flush();
ois.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
private void splitFileDetail(File destFile , RandomAccessFile raf) throws Exception {
byte b[] = new byte[1024];
int lens = 0;
//如果文件目录不存在,则创建
if(destFile.getParentFile().exists() == false){
destFile.getParentFile().mkdirs();
}
BufferedOutputStream bos = null;
try {
raf.seek(currentTotal);//设置开始读取的位置
long currentMax = raf.getFilePointer() + this.blockLength;
bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(destFile));
while ((lens = raf.read(b)) != -1) {
//判断文件读取的大小,避免已经读取超过每块的大小了
if (currentTotal + lens > currentMax) {
break;
}
bos.write(b, 0, lens);
currentTotal += lens;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new Exception(e);
}finally{
if(bos != null){
try {
bos.flush();
bos.close();
} catch (Exception e2) {
e2.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
/**
* 根据文件名称获取文件后缀
* @param fileName 文件名称
* @return 返回.zip或.exe等
*/
private String getFileSuffix(String fileName){
int index = fileName.lastIndexOf(".");
if(index == -1){
return "";
}
return fileName.substring(index);
}
/**
* 获取文件大小
* @param srcFile 源文件
* @return 文件大小long类型
*/
private long getFileLength(File srcFile){
return srcFile.length();
}
}
package cn.chendd.core;
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 合并文件
* @author chendd
*
*/
public class MergeFile {
/**
* 合并文件
* @param propFile 分割文件的属性文件路径
*/
public static void mergeFile(String propFile) throws IOException,
FileNotFoundException, ClassNotFoundException {
File file = new File(propFile);
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(file));
Object obj = ois.readObject();
if(obj instanceof Map == false){
System.out.println("文件以及损坏");
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Map<String , Object> propMap = (Map<String, Object>) obj;
String fileName = (String) propMap.get("fileName");//源文件名称
/**文件大小,科学一点的判定可以判定当前磁盘可用存储空间是否可以容纳本次还原文件**/
//碎片文件
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<String> partList = (List<String>) propMap.get("partList");
File srcFile = new File(file.getParent() + File.separator + fileName);
if(srcFile.exists()){
srcFile.delete();
}
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(srcFile, true));
byte b[] = new byte[1024];
for (String partName : partList) {
String filePath = file.getParent() + File.separator + partName;
//循环读取文件
InputStream is = new FileInputStream(filePath);
int lens = 0;
while((lens = is.read(b)) != -1){
bos.write(b , 0 , lens);
}
is.close();
}
bos.flush();
bos.close();
}
}
该程序已经有更科学与专业的其它实现版本,如有需要请关注本站其它文章或者与作者联系。
点赞











 欢迎来到陈冬冬的学习天地 | 学习与经验整理分享平台
欢迎来到陈冬冬的学习天地 | 学习与经验整理分享平台